Temporomandibular joint disorders can be a source of significant discomfort and confusion. Many people mistakenly use TMJ and TMD interchangeably, but understanding the difference between these terms is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment. This article aims to clarify these terms, explore the symptoms and causes of TMD, and provide an overview of treatment options available. Whether you’re searching for answers to “what is TMJ” or “what is TMD,” we’ve got you covered.
What is TMJ?
Definition and Function of TMJ
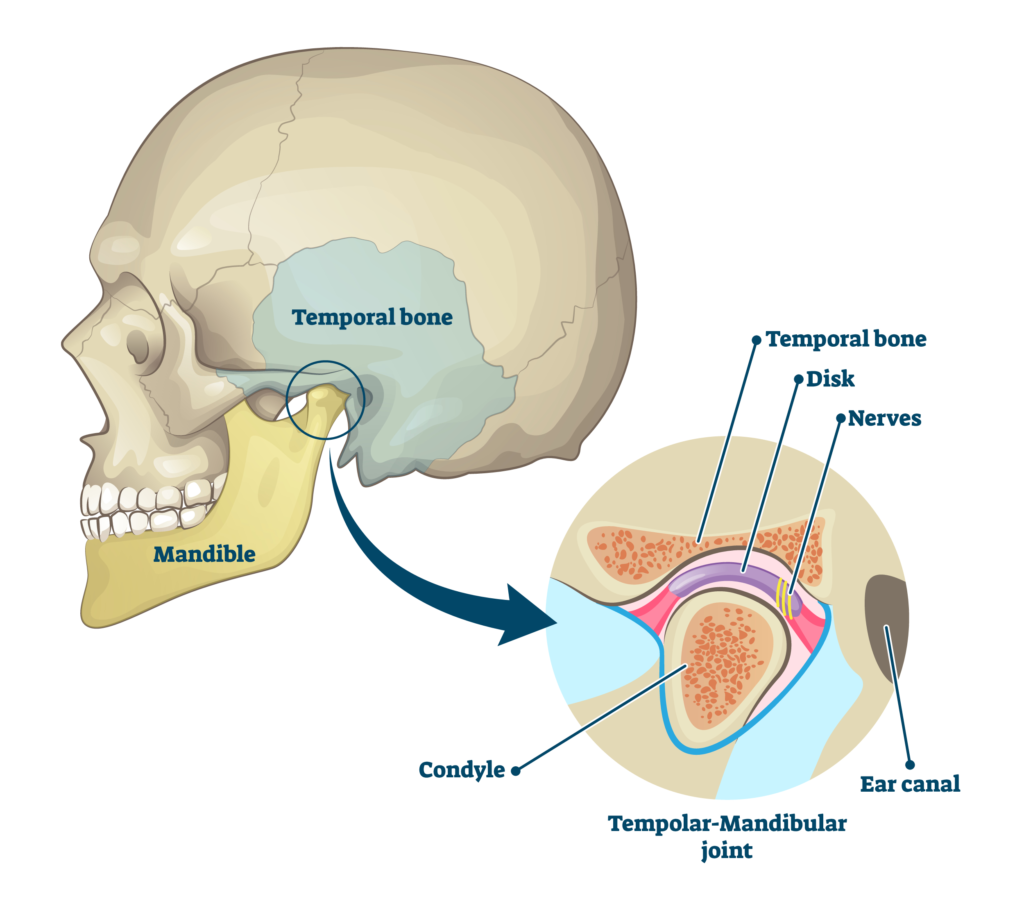
The term TMJ stands for temporomandibular joint. This critical joint connects your jawbone to your skull, allowing you to perform essential functions such as chewing, speaking, and yawning. Located on either side of your head, just in front of your ears, the TMJ is one of the most complex joints in the body due to its ability to move both up and down and side to side.
Anatomy of the Temporomandibular Joint
The temporomandibular joint is a hinge-like structure composed of several key components, including bones, muscles, and ligaments. The main parts include the mandibular condyle (the rounded end of the jawbone), the articular disc (a small, cushioning pad), and the temporal bone of the skull. These components work together to facilitate smooth jaw movements.
What is TMD?
Definition and Causes of TMD
TMD, or temporomandibular disorder, refers to a group of conditions that affect the temporomandibular joint and the muscles controlling jaw movement. These disorders can arise from various causes, including injury to the jaw or head, arthritis, stress, and teeth grinding or clenching.
Types of TMD
TMD can be categorized into three main types:
- Myofascial Pain: Involves discomfort or pain in the muscles that control jaw function.
- Internal Derangement: Refers to a misalignment or displacement of the articular disc or a dislocated jaw.
- Arthritis: Includes degenerative or inflammatory joint disorders affecting the TMJ.
Understanding the type of TMD you have is essential for determining the most effective treatment plan.
Key Differences Between TMJ and TMD
Terminology Differences Between TMJ and TMD
The primary distinction lies in the terminology. TMJ refers to the joint itself, while TMD encompasses the disorders affecting this joint. Confusion often arises because people use TMJ to describe the disorder, but technically, TMJ is a part of your anatomy, whereas TMD refers to the condition.
Functional Differences Between TMJ and TMD
Functionally, the TMJ allows for the movement and function of the jaw. In contrast, TMD involves dysfunction of this joint, leading to symptoms such as pain, limited movement, and clicking sounds. Recognizing this difference is crucial for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Symptoms of TMD
Common Symptoms of TMD
TMD can manifest through a variety of symptoms, including:
- Jaw pain or tenderness
- Headaches or migraines
- Clicking, popping, or grating sounds when opening or closing the mouth
- Difficulty chewing or biting
- Ear pain or ringing in the ears (tinnitus)
- Locking of the jaw joint, making it difficult to open or close the mouth
When to Seek Help for TMD
If you experience persistent jaw pain, frequent headaches, or any of the symptoms listed above, it’s essential to seek professional help. Early intervention can prevent the condition from worsening and improve your quality of life.
Diagnosis of TMD
Diagnostic Procedures for TMD
Diagnosing TMD typically involves a combination of physical exams and imaging tests. Your healthcare provider may:
- Examine your jaw for tenderness, clicking, or locking.
- Observe the range of motion in your jaw.
- Take X-rays, CT scans, or MRI scans to get a detailed view of the joint and surrounding tissues.
Role of Healthcare Professionals in Treating TMD
Dentists and specialists play a vital role in diagnosing and treating TMD. They can develop a personalized treatment plan based on the severity and type of your disorder, helping you manage symptoms effectively and improve joint function.
Treatment Options for TMD
Non-Surgical Treatments for TMD
Several non-surgical treatments can alleviate TMD symptoms:
- Medications: Pain relievers, anti-inflammatory drugs, and muscle relaxants can help reduce pain and inflammation.
- Physical Therapy: Exercises and techniques designed to strengthen and stretch the jaw muscles.
- Dental Appliances: Bite guards or splints to prevent teeth grinding and correct jaw alignment.
- Stress Management: Techniques such as relaxation exercises, counseling, or cognitive behavioral therapy to manage stress and reduce muscle tension.
Surgical Treatments for TMD
In severe cases, surgical intervention may be necessary. Options include:
- Arthrocentesis: A minimally invasive procedure to flush out the joint.
- Arthroscopy: A procedure using a small camera to diagnose and treat joint issues.
- Open-Joint Surgery: A more invasive option to repair or replace the joint when other treatments fail.
Self-Care Tips for TMD
In addition to professional treatments, self-care practices can help manage TMD symptoms:
- Jaw Exercises: Gentle stretching and strengthening exercises recommended by your healthcare provider.
- Heat and Cold Therapy: Applying heat or cold packs to the jaw to reduce pain and swelling.
- Dietary Changes: Eating soft foods and avoiding hard, chewy, or sticky foods.
- Good Posture: Maintaining good posture to reduce strain on the jaw.
Key Takeaways
Understanding the difference between TMJ and TMD is essential for accurate diagnosis and treatment. TMJ refers to the joint itself, while TMD encompasses disorders affecting this joint. If you experience symptoms of TMD, such as jaw pain, headaches, or clicking sounds, seek professional help to manage the condition effectively.
For personalized diagnosis and treatment, contact the Ottawa TMJ & Sleep Apnea Clinic. Our team of experts is dedicated to providing comprehensive care for TMD, helping you achieve relief and improve your quality of life. Don’t let TMD symptoms interfere with your daily activities—reach out to us today for a consultation.